The genus Paraphysomonas comprises solitary, colourless flagellates, spherical to slightly oval cells, covered by numerous spine scales with usually circular, rarely oval, base-plate approximately orthogonal to a long thin central spine. Spine unbranched, unwinged, many times narrower than base-plate even at itsbase. Base-plate entire or with small perforations, of varying distribution but no large lacunae. Spine length varies from just longer than to several times base-plate width. Separate plate scales generally absent, but if present closely resemble spine-scale base-plate but with spine missing, usually larger in diameter and no distinctive morphology. The cells bear two flagella of unequal length. They are found either as freely swimming cells or attached to the substratum via a slender posterior stalk.
Paraphysomonas species feed on various different organisms, such as bacteria, diatoms or small chlorococcalean algae. The prey is ingested at the base of the flagella after being pulled in via the motion of the long flagellum, the food is incorporated into vacuoles within a few seconds. Undigested particles are extruded around the posterior end of the cell.
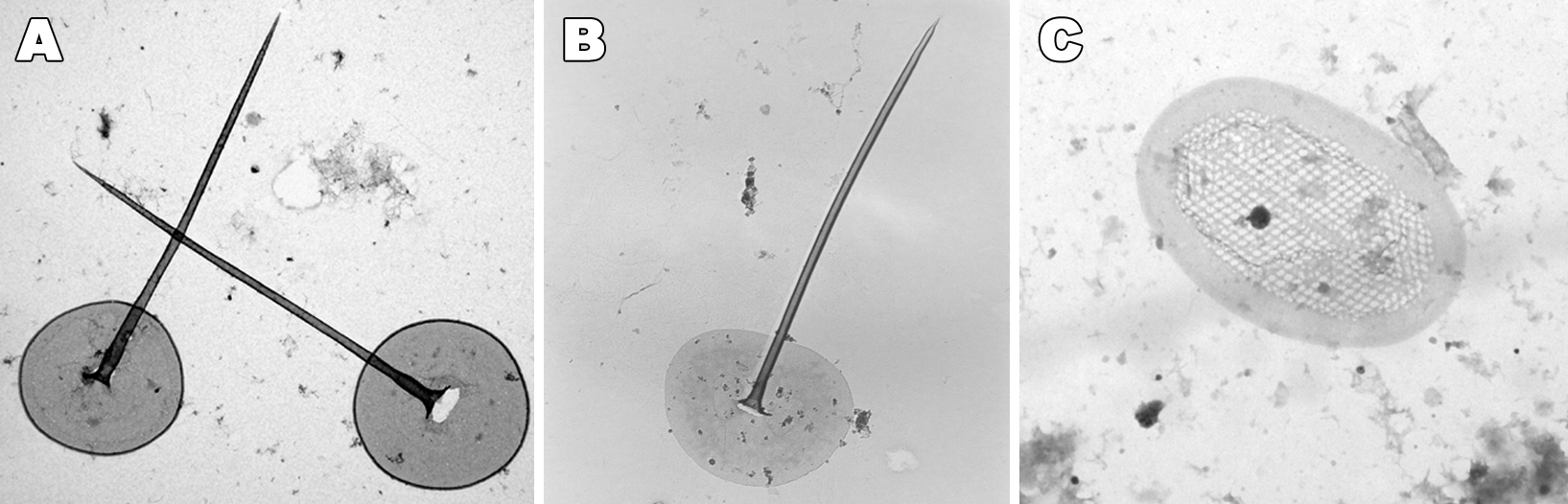 |
Paraphysomonas siliceous structures. A. Circular flat disc scale with a centrally protruding tapering spine and thickened rim (P. vestita morphotype) B. Circular flat disc scale with a central spine (P. imperforata). C. Bowl-shaped, elliptical scale with a wide rim (P. punctata). |
